Forecasting Global Horizontal Irradiance Using Deep Learning
A comprehensive benchmark of 10 deep learning architectures for short-term solar forecasting in Ho Chi Minh City, prioritizing both accuracy and computational efficiency.
Project Details
Role
Researcher
Team Size
Individual
Duration
Feb 2025 - May 2025
Overview
Developed a comprehensive deep learning framework for forecasting Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. This research serves as a benchmark study comparing 10 neural network architectures—ranging from traditional baselines (LSTM, TCN, 1D-CNN, CNN-LSTM, MLP) to cutting-edge models (Mamba, Transformer, iTransformer, TSMixer, Informer)—using a decade of satellite-derived data.
The project explicitly balances predictive accuracy with computational sustainability, aiming to deploy high-performance models on resource-constrained edge devices in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs 7 and 13).
Problem Context
Accurate solar irradiance forecasting is critical for:
- Grid Stability: Mitigating the intermittency of solar power for reliable integration.
- Energy Trading: Enabling precise day-ahead and intra-day market bidding.
- Sustainability: Reducing the carbon footprint of AI by optimizing model efficiency.
Ho Chi Minh City's tropical climate poses unique challenges, with rapid cloud formation and intense monsoon seasons creating high volatility in solar irradiance (GHI).
Data Pipeline
Problem Formulation
The project models GHI forecasting as a supervised time-series regression task. Given a historical sequence of input vectors with a lookback window , the objective is to learn a mapping function that predicts the irradiance for horizon :
where represents the learnable parameters of the neural network optimized for grid stability management.
Data Source & Processing
- Source: National Solar Radiation Database (NSRDB) Himawari-7 satellite data (PSM v3).
- Period: 10 years of hourly measurements (2011–2020).
- Scale: 87,600 timesteps × 105 grid cells (approx. 4km resolution).
- Split: Chronological split to prevent look-ahead bias: Training (2011–2018), Validation (2019), Test (2020).
Feature Engineering
- Target: Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI).
- Inputs: 24-hour lookback window (L=24) to predict 1-hour ahead (H=1).
- Physics-Informed Features:
- Clearsky GHI: Theoretical maximum irradiance calculated via solar zenith angle.
- Nighttime Mask: Binary mask () to filter trivial zero-value predictions.
- Cyclical Encoding: Sin/Cos transformations for hour, day, and month to preserve temporal continuity.
Key Results
Evaluation Metrics
To rigorously assess performance, we employed standard statistical metrics. The Mean Squared Error (MSE) was used as the primary loss function to penalize large errors, while the Coefficient of Determination () measured variance explanation:
where is the ground truth, is the prediction, and is the mean of observed data.
Comprehensive Model Comparison
| Model | MSE ↓ | RMSE ↓ | MAE (W/m²) ↓ | R² ↑ | Speed (samples/sec) ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer | 2816.77 | 53.07 | 24.26 | 0.9696 | 239,871 |
| Informer | 2846.86 | 53.36 | 24.90 | 0.9692 | 117,882 |
| TSMixer | 2848.61 | 53.37 | 25.66 | 0.9692 | 88,357 |
| TCN | 2856.48 | 53.45 | 25.32 | 0.9691 | 644,131 |
| LSTM | 2859.22 | 53.47 | 26.87 | 0.9691 | 215,547 |
| iTransformer | 2869.81 | 53.57 | 25.62 | 0.9690 | 272,867 |
| Mamba | 3006.05 | 54.83 | 25.84 | 0.9675 | 193,084 |
| MLP | 3165.89 | 56.27 | 27.84 | 0.9658 | 5,642,588 |
| CNN-LSTM | 3274.12 | 57.22 | 29.81 | 0.9646 | 310,191 |
| 1D-CNN | 3549.03 | 59.57 | 32.44 | 0.9617 | 996,542 |
Key Findings:
- Transformer Dominance: Outperformed all models (approx. 1.4% MSE reduction vs. TCN), excelling at capturing short-term volatility via self-attention.
- TCN Efficiency: The best "basic" model, offering a robust trade-off with 2.7× higher throughput than Transformer.
- Mamba's Limitation: Despite theoretical linearity, Mamba struggled with peak daytime fluctuations, lagging behind attention-based models in accuracy.
Daytime vs. Nighttime Analysis
The study evaluated performance separately for day and night to ensure robust benchmarking:
- Daytime: Transformer achieved the lowest error (MSE: 5653.55) and highest R² (0.9313), proving its ability to model complex cloud dynamics.
- Nighttime: Transformer and TCN correctly suppressed noise (R² > 0.64). In contrast, Mamba performed poorly at night, exhibiting a negative R² (-2.43), indicating it failed to consistently suppress zero-value predictions.
Model Compression & Efficiency
To enable deployment on edge devices (e.g., solar farm controllers), three compression strategies were applied to the Transformer.
| Compression Method | Model Size (MB) | Reduction | Latency (ms) | MAE (W/m²) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (FP32) | 1.07 | — | 3792.13 (CPU) | 24.26 | Reference performance |
| Int8 Quantization | 0.44 | 64.0% | 519.88 | 25.24 | Best CPU Trade-off |
| Int4 Quantization | 0.11 | 91.0% | 589.69 | 25.60 | High latency due to overhead |
| FP16 (GPU) | 0.65 | 46.0% | 22.02 | 24.25 | Best for High-Perf Edge |
| Pruning (10% Sparsity) | 1.07 | 0.0% | 3808.80 | 40.66 | Accuracy degraded |
| Pruning (50% Sparsity) | 1.07 | 0.0% | 3857.31 | 176.21 | Method Failed |
| Distilled Student | 0.82 | 23.5% | 3081.46 | 23.78 | Outperformed Teacher |
Key Technical Insights:
- Distillation Works: The Distilled Student (MAE: 23.78) outperformed not only the Teacher (MAE: 24.26) but also an identical Student trained from scratch (MAE: 25.35). This confirms distillation acts as a powerful regularizer.
- Pruning Failed: Structured pruning (10–50%) was ineffective. Physical model size remained unchanged (1.07 MB) due to PyTorch storage mechanics, and error spiked dramatically (MAE: 176.21 at 50% sparsity).
- Quantization Overhead: While Int4 quantization achieved massive size reduction (91%), it actually increased latency compared to Int8, likely due to the computational cost of unpacking 4-bit integers.
Explainability (SHAP)
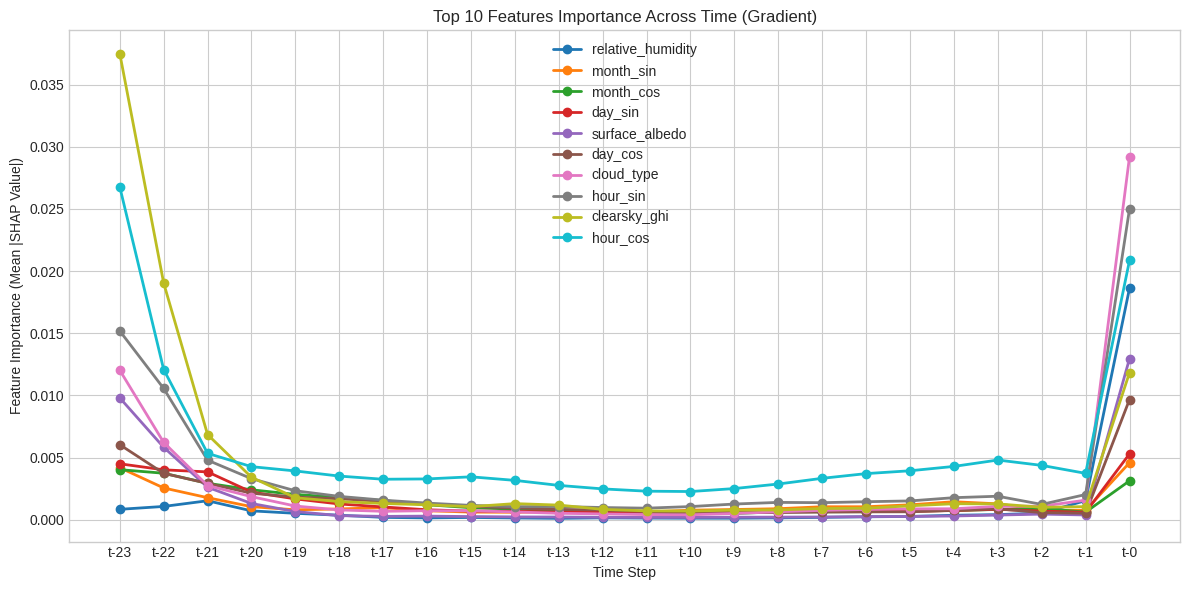
SHAP analysis revealed fundamental differences in how architectures "reason" about time:
- Transformer (Recency Bias):
- Focuses almost exclusively on (current timestep).
- Heavily relies on immediate predictors:
hour_cos,cloud_type, andhour_sin.
- Mamba (U-Shaped Periodicity):
- Exhibits a distinct U-shaped attention pattern, valuing both the immediate past () and the distant history ().
- Explicitly leverages the 24-hour periodic nature of solar cycles, heavily weighting
clearsky_ghifrom the previous day.
Key Predictor: clearsky_ghi was identified as the single strongest feature, providing the physical baseline for all models.
Future Directions
- Extend to multi-horizon forecasting: Move beyond 1-hour ahead prediction to longer horizons (e.g., 24–48 hours) and re-evaluate architectures like Mamba under longer-context settings where linear-time sequence modeling may become more advantageous.
- Richer atmospheric & satellite inputs: Incorporate real-time Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and raw satellite-imagery channels to better capture the effects of urban haze and fine-grained cloud structure that can drive short-term irradiance variability.
Conclusion
This research successfully establishes a benchmark for solar forecasting in tropical climates, demonstrating that while Transformers offer superior accuracy for short-term prediction, TCNs provide a highly efficient alternative for high-throughput systems. Crucially, the study proves that high-performance deep learning models can be effectively compressed via Knowledge Distillation to run on edge hardware without accuracy loss. By combining rigorous benchmarking with explainability and model compression, this framework offers a practical blueprint for sustainable, AI-driven energy management in developing smart cities.
Note
Read the full paper on arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.23898
Key Achievements
- Achieved state-of-the-art accuracy with Transformer model (MSE: 2816.77, R²: 0.9696)
- Proven Knowledge Distillation success: Distilled Student outperformed both the Teacher and a Student trained from scratch
- Benchmarked 10 architectures using 10 years of NSRDB satellite data (87,600 timesteps)
- Identified critical deployment constraints: Int4 quantization reduced size by 91% but increased latency