Enhancing Diffusion Face Generation with Contrastive Embeddings and SegFormer Guidance
Benchmark study comparing UNet and DiT architectures for unconditional generation, with novel InfoNCE contrastive loss and SegFormer-based segmentation for attribute-conditioned face synthesis.
Project Details
Role
Team Lead, Researcher
Team Size
4
Duration
Mar 2025 - Jun 2025
Overview
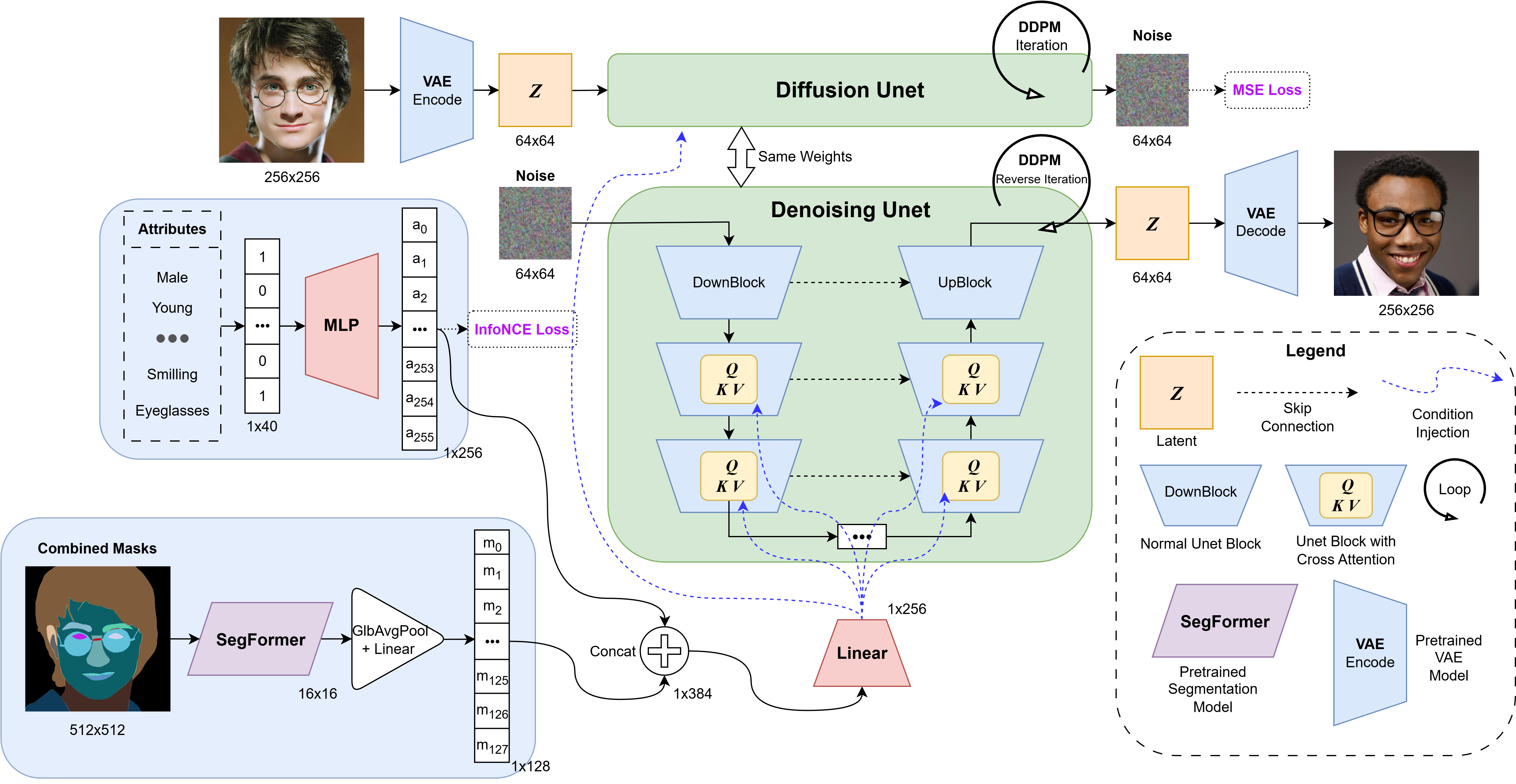
A comprehensive benchmark of diffusion models for human face generation on the CelebAMask-HQ dataset, evaluating both unconditional and conditional pipelines. Building on multi-conditioning approaches, our main contributions are the integration of InfoNCE loss for attribute embedding and the adoption of a SegFormer-based segmentation encoder, enhancing semantic alignment and controllability of attribute-guided synthesis.
Research Motivation
Diffusion models have become state-of-the-art for high-fidelity image synthesis, but generating controllable human faces with fine-grained attribute control remains challenging, especially with limited training data. We investigated how contrastive learning and advanced segmentation encoding can improve attribute-guided face generation.
Methodology
Unconditional Generation
- UNet Architectures: Implemented multiple UNet variants with varying depths (4-6 blocks) and attention placements
- DiT (Diffusion Transformer): Explored transformer-based backbone as alternative to UNet
- EMA Stabilization: Applied Exponential Moving Average on model weights, reducing FID by ~19 points
- Training: DDPM framework at 128×128 resolution with learning rates 1e-5 to 5e-4
Conditional Generation with LoRA
- Fine-tuned Stable Diffusion v2 using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)
- Added rank-decomposed matrices to UNet attention layers for efficient adaptation
- VQ-VAE encoder compresses 512×512 images into 64×64×4 latents
- Compared conditional vs unconditional fine-tuning approaches
Attribute-Conditioned Generation
- Latent Space Encoding: Pre-trained VQ-VAE compresses images to 64×64 latent space
- Conditional UNet: UNet2DConditionModel with 256D embeddings via cross-attention
- Attribute Embedder: MLP maps 40D multi-hot attribute vectors to 256D embeddings
- Novel InfoNCE Loss: Contrastive objective ensures embeddings capture semantic relationships
Segmentation Guidance with SegFormer
- Replaced baseline ResNet-18 mask encoder with pretrained SegFormer
- Processes combined segmentation masks into 128D spatial embeddings
- Joint attribute + segmentation embeddings concatenated and projected (512→256D)
- Provides precise spatial and attribute control for face synthesis
Key Innovation: InfoNCE for Attribute Embedding
The InfoNCE (Noise-Contrastive Estimation) loss trains the attribute embedder to capture semantic relationships. The loss is formulated as:
Where:
- B: Batch size
- sim(·,·): Cosine similarity between embeddings
- τ: Temperature parameter (default 0.07)
- pos: Indices of positive pairs (attribute similarity > 0.8)
Training Process:
- Attribute Similarity: Cosine similarity between multi-hot vectors identifies positive pairs (threshold 0.8)
- Embedding Similarity: Scaled by temperature parameter τ
- Contrastive Learning: Encourages similar attributes to cluster, dissimilar to separate
- Result: More discriminative embeddings that enhance the UNet's conditioning precision
Experimental Results
Unconditional Diffusion
| Model | Configuration | FID ↓ |
|---|---|---|
| UNet-R3 | LR 2e-4, Warmup 3000, EMA | 72.62 |
| UNet-R5 | LR 2e-4, Warmup 3000, EMA | 76.08 |
| UNet-R6 | LR 2e-4, Warmup 1500, EMA | 73.35 |
| UNet-R5 | No EMA | 92.90 |
| DiT-Large | 2.7k samples | 89.90 |
| DiT-Small | 2.7k samples | 94.00 |
Conditional Generation with Attributes
| Configuration | FID ↓ |
|---|---|
| LCUNet3 (Baseline) | 74.07 |
| LCUNet3 + InfoNCE | 70.98 |
| LCUNet3 + InfoNCE + Segmentation | 63.85 |
LoRA Fine-tuned Stable Diffusion v2
| Condition | Inference Steps | FID ↓ |
|---|---|---|
| Conditional (No Tuning) | 50 | 114.73 |
| Conditional + LoRA | 150 | 65.31 |
| Unconditional + LoRA | 50 | 91.32 |
Ablation Study: With and Without InfoNCE loss
The "Without InfoNCE" images (middle) lack clarity, with blurred features, distorted proportions, and unnatural textures. The "With InfoNCE" images (right) are sharper, with better-defined facial features and more accurate attributes generation.

Visual Comparison between LC-UNet-3 with and without InfoNCE loss training.
Key Findings
- Architecture: Deeper UNet variants with mid-level attention achieve superior FID (72.62–76.08)
- EMA Impact: Weight averaging reduces FID by ~19 points (92.90→73.99)
- InfoNCE Benefit: Improves attribute-guided FID from 74.07 to 70.98
- Segmentation Guidance: Adding SegFormer masks further reduces FID to 63.85
- LoRA Efficiency: Conditional LoRA models achieve best FID of 65.31, outperforming unconditional variants
Note
Read the full paper on arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.09847
Key Achievements
- Best unconditional FID of 72.62 with UNet + EMA stabilization
- Best conditional FID of 63.85 with attribute + segmentation conditioning
- Improved attribute-guided FID from 74.07 to 70.98 through InfoNCE loss integration
- LoRA fine-tuned Stable Diffusion v2 achieved FID of 65.31